Water Recycling & Reuse Solutions-
Reduce water footprint, lower operating costs, and improve operational sustainability.
Water Recycle & Reuse Solutions
Freshwater sources in several regions around the world are running out or will run out. Water is necessary to secure an improved quality of life due to the impact of climate change and other environmental issues. However, in a future world where the water sector delivers ‘Water-on-Demand’ solutions in combination with new technologies and new business models, the balance between demand and supply should be in harmony.
What is water reuse?
Water reuse, also known as water recycling, is the process by which wastewater from a variety of sources is treated to be reused for beneficial purposes. After a decade of the ‘proof of principle,’ clients are now actively asking for integrated water reuse solutions which is a seismic shift. Instead of discharging water flowing into the river (which ends up in the sea), a regional water cycle will keep the water in the area where it was originally used and keep the local water buffer at the desired ‘on-demand’ level. This is especially necessary for regions that are already dry.
Nijhuis Saur Industries has the solutions and technologies to reduce, reuse and recover water and resources from wastewater, ground water, cooling water, or other original water sources.



Why apply water reuse?
To cope with water stress, authorities are imposing more and stricter water regulations. As a result, water is becoming more valuable, and its price will increase. Moreover, when an industrial facility reaches a production limitation due to shortages of fresh water, it is no longer a choice but a necessity to reuse ‘waste’ water to continue growth.
Some typical cases to consider water reuse:
- Production limitations due to water shortage.
- Meet Corporate Social Responsibility goals to reduce the water footprint.
- Reduce water disposal costs and/or meet effluent disposal limits.
- Reduce the impact of drought by reusing sewage wastewater.
- Decentralized circular water management for residential areas.
Where and how to apply water reuse to reduce the water footprint?
The continuous battle for more water in the future leaves no other option but to reuse the treated effluent most efficiently. Numerous processes and technical solutions exist for municipal and industrial customers to reuse wastewater. In order to find the right treatment and reuse solution, each industry and application has to be evaluated individually. In several client cases, the production extension has reached its limitations due to limited freshwater resources, reuse of wastewater enables the client to continue their growth.
Applications for water reuse:
- Turn industrial effluent into recycled water.
- Treat and disinfect cooling water for multiple reuse cycles.
- Recover spend CIP fluids from industrial processes.
- Turn rooftop rainwater into household water residential water reuse.
- Turn sewage wastewater into irrigation and process water.
- Turn groundwater into drinking water or other industrial process purposes.
- Turn seawater into drinking water.

Nijhuis Saur Industries Technology overview
Depending on the application, technologies can either be applied to industrial wastewater, groundwater, cooling water, condensate water treatment, or decentralized sewage water and sanitation treatment.
Industrial Wastewater
Nijhuis Saur Industries and Econvert offer customized solutions based on in-depth process knowledge. We design and construct the following water and biogas treatment plants.
- BIOCTOR-MBR
A sludge water separation system using a flat plate or hollow fiber membrane modules for wastewater. This can be part of tertiary treatment or the start of pre-treatment for the membranes, including CIP and flush water recovery. - NMS-UF – Ultrafiltration
This unit is a superior barrier for viruses and bacteria removal and a solid pre-treatment for reverse osmosis. - NMS-dNF – Direct Nanofiltration
This combines two steps: ultra and microfiltration. This unit can be implemented to remove color, bacteria, and viruses for drinking water and wastewater applications. - NMS-RO – Reverse Osmosis
This is the last membrane step before disinfection for producing, e.g., drinking water. The unit removes dissolved components, such as ions, heavy metals, TOC, and viruses.
- NMS-EDR – Electrodialysis Reversal
The Nijhuis EDR unit removes all kinds of dissolved materials, such as salt. The unit can be adjusted to remove the salt with electricity and use a reduced amount of chemicals. - MLD/ZLD – Evaporators
A smart combination and selection of solutions such as evaporation, crystallizer, membrane, and EDR solutions towards zero liquid discharge. This is sometimes necessary to cope with the brine generated from reverse osmosis. Minimizes brine for disposal.
AECO-CIP – CIP Recovery
The AECO-CIP recovery system treats spent CIP solutions (i.e., hot soda based). This unit lets you reuse spent CIP fluids and (hot)water.
.
Reverse Osmosis Range Specification Table
| Pv number | Modules | Feedflow | Permaete
Range |
||
| Skid type | Nr | Nr | m3/h | 60% 80% | m3/h |
| NMS-RO-12 | 3 | 12 | 12 | 7 to 10 | m3/h |
| NMS-RO-18 | 3 | 18 | 18 | 11 to 14 | m3/h |
| NMS-RO-24 | 6 | 24 | 24 | 14 to 19 | m3/h |
| NMS-RO-36 |
6 |
36 | 36 | 22 to 29 | m3/h |
| NMS-RO-54 | 9 | 54 | 54 | 32 to 43 | m3/h |
| NMS-RO-72 | 12 | 72 | 72 | 43 to 58 | m3/h |
| NMS-RO-90 | 15 | 90 | 90 | 54 to 72 | m3/ |


Large poultry processing plant reusing 1,056,688 gpd

Large cosmetic plant reuses approximately 19,812,904 gallons per year
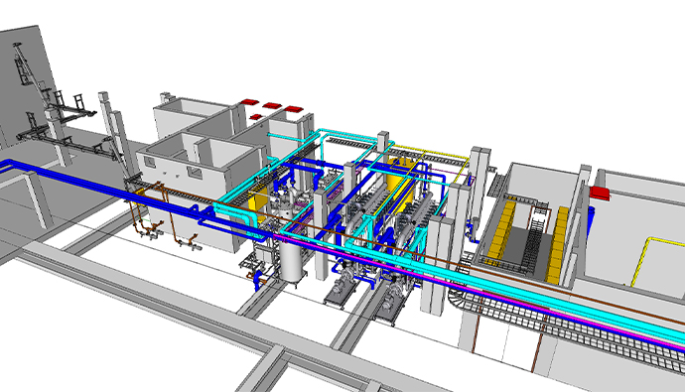
Paper production plant designed to reuse around 396,258 gpd (plant under construction)

Visitor center for a heritage site reusing around 6604 gpd for toilet flushing
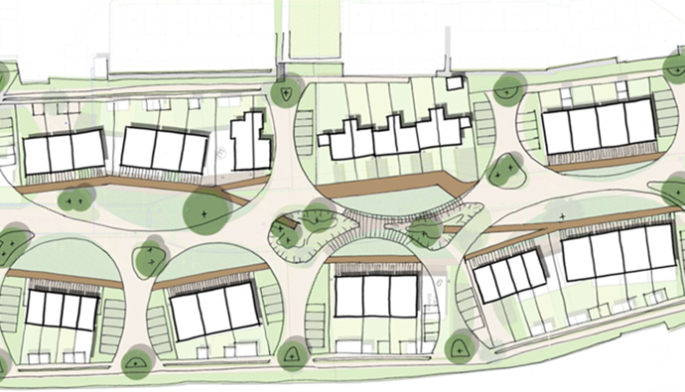
New residential construction turning rain water from the rooftop into sanitation water. Wastewater from the houses is also treated for infiltration in the soil.

Cooling tower water reuse for major law firm with 66% water recycling and reduced water consumption by 13,208,603 gallons



